What is the continuous carbonization process?
Continuous carbonization process is a modern method of converting biomass (like sawdust, rice husks, coconut shells, bamboo, straw, nutshells, etc.) into charcoal (such as machine-made charcoal or activated carbon) and combustible gases. This is done by heating the materials at high temperatures in a low-oxygen or oxygen-free environment.
To meet the needs of large-scale and automated charcoal production, Shuliy Machinery has carefully developed and launched the Continuous Carbonization Furnace. This machine features a sealed design, with continuous feeding and discharging, making it ideal for the efficient carbonization of various biomass materials. It is widely used for processing sawdust, rice husks, coconut shells, nutshells, crop stalks, and more, turning waste into valuable resources.




This process is centered on stable high-temperature pyrolysis, combined with intelligent control, heat recovery, and exhaust gas purification technologies. Together, they form an eco-friendly, efficient, and highly automated charcoal production solution.
Compared with traditional batch carbonization, the continuous carbonization process offers significant advantages in energy efficiency, environmental protection, and output capacity.
Key Features of the Continuous Charcoal Carbonization Furnace
Continuous Feeding & Discharging
Raw materials are fed and discharged automatically, supporting uninterrupted, large-scale production.
Sealed and Safe Design
The entire carbonization takes place in a closed chamber, reducing smoke, gas leakage, and fire risks.
Energy Efficient
The combustible gas produced during carbonization is reused as fuel, lowering external energy costs.
Smart Control System
Equipped with automated temperature control and feeding systems for precise operation.
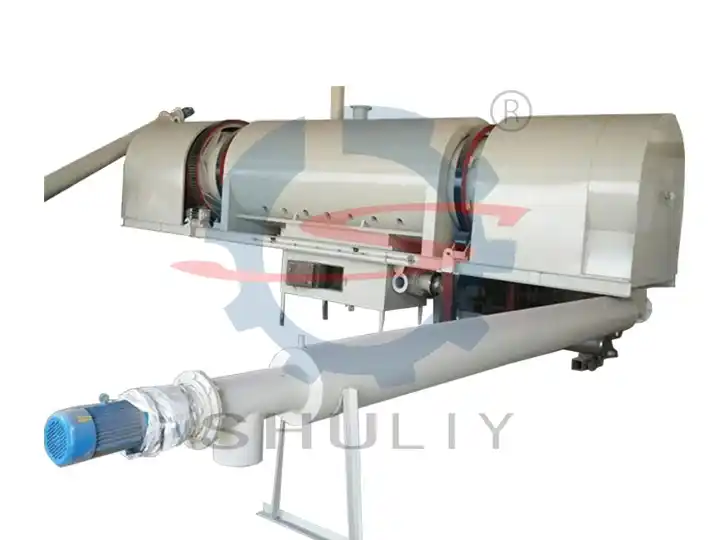

Carbonization Process Flow
Raw Material Preparation
- Crushing: Materials larger than 15 cm need to be crushed.
- Drying: Moisture content should be below 15% for optimal results.
- Feeding: Use screw conveyors or belt conveyors to load materials into the furnace.
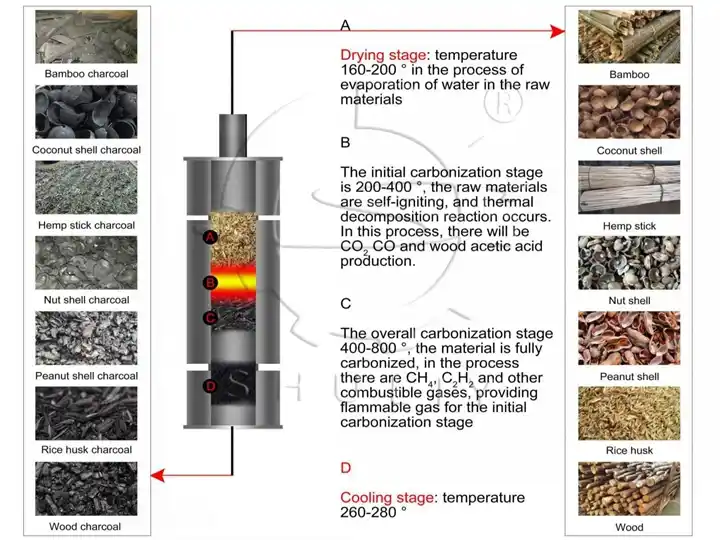
High-Temperature Carbonization (400–800°C)
The biomass undergoes pyrolysis, breaking down into charcoal and gases:
- Drying Zone (160–200°C): Moisture evaporation
- Pyrolysis Zone (200–400°C): Organic matter begins to decompose
- Carbonization Zone (400–800°C): Charcoal forms, and gas is released
- Cooling Zone (260–280°C): Prevents re-ignition
Combustible Gas Recovery & Reuse
Gases like CO, H₂, and CH₄ are cleaned and reused for heating, reducing the need for extra fuel.
Charcoal Cooling & Discharging
A cooling system (screw or water cooling) brings down the charcoal temperature. Finished charcoal is then automatically discharged.
Exhaust Gas Treatment
Exhaust gases are filtered, condensed, and purified before being safely released, meeting environmental standards.
Advantages of the Continuous Carbonization Process
- High Output: Daily capacity can reach several tons—ideal for industrial use.
- Low Energy Consumption: Uses its own gases for heating.
- Eco-Friendly: Clean emissions with no visible smoke or strong odor.
- Fully Automated: Less manual work, safer operation, consistent quality.
- Wide Application: Handles various agricultural, forestry, and industrial organic wastes.
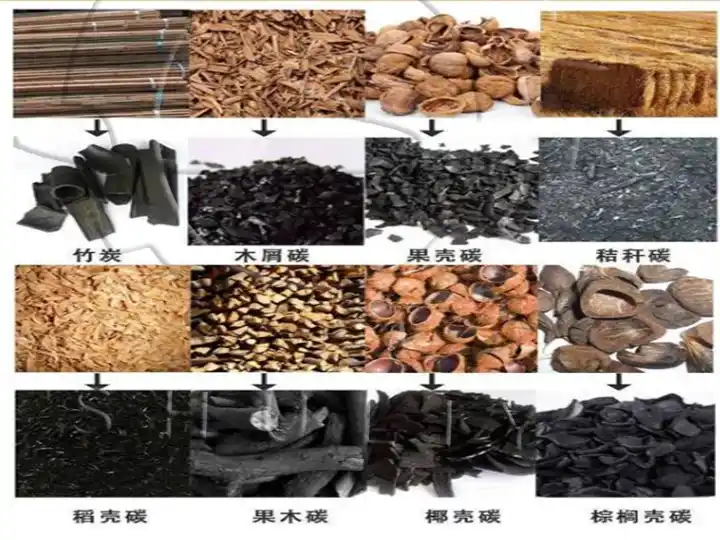
Suitable Raw Materials
- Biomass (e.g., sawdust, peanut shells, corn stalks, rice husks)
- Agricultural Waste (e.g., sugarcane bagasse, sorghum stalks, cotton stems)
- Forestry Waste (e.g., bamboo, tree branches, palm shells)
- Other Organic Waste (e.g., distiller’s grains, corn cobs, dry leaves)
- Industry By-products (e.g., coffee grounds, apricot shells, herbal residue)
- Various Plant Stems (e.g., sunflower shells, yam vines, hemp stalks)
- Urban Sludge & Paper Mill Waste (requires pre-treatment)
- Industrial Organic Waste (after dehydration and crushing)

Equipment Recommendation
Model: SL-CF1200
Diameter: 1200mm
Capacity: 1200-2000 kg/h
Main Power: 20kw
Carbonization Temperature: 500-800℃
Fan Power(kw): 5.5kw
Production date: 20 working days
Transportation: By sea

Application Fields
- Machine-made charcoal production: For BBQ charcoal, heating fuel, etc.
- Pre-carbonization of activated carbon materials
- Carbon-based fertilizer manufacturing
- Waste-to-resource utilization: Harmless carbonization of agricultural straw and municipal waste
- Carbon sinks and carbon trading: Carbon sequestration to support carbon peaking and neutrality
